Spend sufficient time browsing the and one could ask, “Is green construction losing its mojo?”
Announcements made by governments on either side of the U.S.-Canada border might appear pessimistic about the priority being given to addressing carbon reduction and various other environment issues, including those impacting the building industry.
The good news is construction material innovation continues. New ideas that address carbon reduction, both embodied and through operations, are finding moral and financial support.
, the Rocky Mountain Institute’s global climate tech accelerator, welcomed 18 new start-ups from six countries across four continents this past August. Third Derivative identifies, funds and scales climate tech globally, and unites and aligns investors, corporations and experts with the world’s most promising climate tech start-ups. In this way, Third Derivative bridges finance and resource gaps to increase the speed that breakthrough products can reach the market.
“From scalable bamboo building systems to modular green hydrogen, recyclable wind turbines to zero-emission cooling, these start-ups represent the cutting edge of global climate tech innovation,” Rushad Nanavatty, Third Derivative’s managing director.
Four new innovations from the latest Third Derivative would be of particular interest to the construction industry.

IntelliKoat™ transforms building envelopes with adaptive two-layer roof coatings that offer a number of benefits. IntelliKoat applications cut Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions and HVAC energy use by up to 30 per cent and extend roof life by up 20 years. IntelliKoat’s patented dual-layer technology performs year-round across diverse climates, offering a scalable, cost-effective retrofit solution for commercial building owners seeking energy savings, durability and climate resilience.
develops scalable bamboo panel systems for diverse applications, from cool roofs with reflective surfaces that improve thermal comfort in hot climates, to low-carbon interiors and structural sandwich panels. Designed for adaptability and mass production, Ocean’s bamboo panels enable both climate adaptation and decarbonized construction while simultaneously cutting emissions and preserving biodiversity.
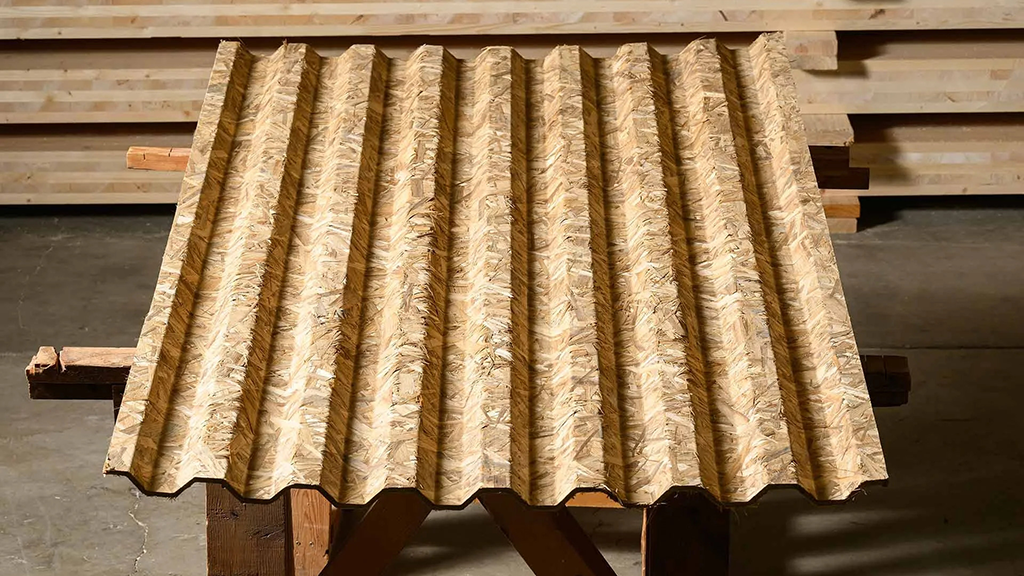

Bamboo is a tough strong replacement for many traditional building materials like lumber. At the same time, bamboo is one of the fastest growing plants in the world, regenerating in a fraction of the time than that of trees, making it a sustainable choice.
“The panels are structurally strong, less expensive than reinforced concrete, and feature a paint coating that keeps them cooler,” the company . “If properly maintained with paint or stains, the panels should last up to 25 years.”
The carbon impact of concrete is well-documented and well-discussed. In its ongoing search to develop more earth and climate-friendly concrete mixtures, has developed the patented Clearwash process. This transforms biomass waste into carbon-storing bioaggregates that are chemically compatible with concrete.
As an alternative to sand, bioaggregates reduce dependency on the world’s diminishing natural sand resources and replace it with locally-sourced bioaggregates that are both renewable and can be harvested annually with no changes to existing processes.
These low-cost, low capex concrete bioaggregate solutions can directly reduce emissions by about 40 per cent, and can be used as ready-mix, drywall alternatives, insulated panels and for 3D concrete printing.
delivers fully integrated heating, cooling and hot water systems on a subscription basis that intelligently adapt to each building’s unique thermal needs. Aris’ all-in-one modular system replaces the furnace, A/C, and water heater without any duct maze or refrigerant line sets.
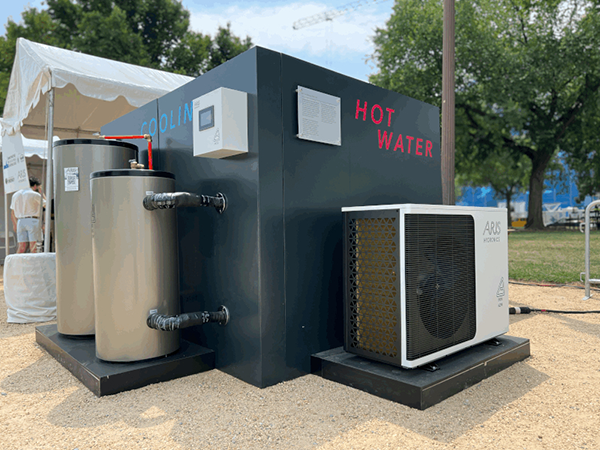

Then, using the company’s first-of-its-kind Thermal-as-a-Service platform, dozens of sensors and data points are continuously learning and optimizing, with embedded controls and cloud orchestration balancing heating, cooling and hot-water demands in real time. This lowers upfront costs and delivers real-time optimization, maintenance and comfort.
Third Derivative is supported by major corporate sponsors across many industries, like FedEx, Netflix, AT&T and Shell. Such a diverse range of support is critical to Third Derivative’s objectives, the organization says.
“Funding and access are based on who you know, and what they know. At Third Derivative, we know we can only achieve the rapid, massive tech scaling needed to address climate change by giving more breakthrough thinkers a chance to participate and prosper.”
“Third Derivative is taking on the critical work to identify and accelerate the availability and viability of such clean energy innovations and connecting them with companies to develop and deploy them at scale,” says Mitch Jackson, vice-president, environmental affairs and chief sustainability officer at the FedEx Corporation.
John Bleasby is a freelance writer. Send comments and Inside Innovation column ideas to editor@dailycommercialnews.com.





Recent Comments
comments for this post are closed